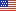
Thirty-four years ago, on April 28, 1983, NOAA launched the GOES-6 satellite -- the second spacecraft in the second-generation of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites!

Happy anniversary GOES-6!
Thirty-four years ago, on April 28, 1983, NOAA launched the GOES-6 satellite! Known as GOES-F prior to launch, GOES-6 was the second spacecraft in the second-generation of GOES-series satellites and served in the GOES-West position.
Designed to replace GOES-4, GOES-6 was initially placed in geostationary orbit directly over the Pacific along the equator at 136 West. After GOES-5 failed, it was moved to a central location at 98 West. When GOES-7 was placed in service, it returned to its original position.
The cylindrical GOES-6 spacecraft was 85 inches in diameter, 138 inches high and weighed 874 pounds. Its sides were covered by 15,000 solar cells which, along with nicad batteries, provided the satellite's power. Protruding from GOES-6's base was its primary instrument -- the Visible Infrared Spin Scan Radiometer Atmospheric Sounder (or VAS), which provided both day and night imagery of cloud conditions as well as temperature and moisture profiles over its full-disk profiles of Earth. Unfortunately, the VAS imager failed on January 21, 1989, rendering direct readout images and soundings unavailable.
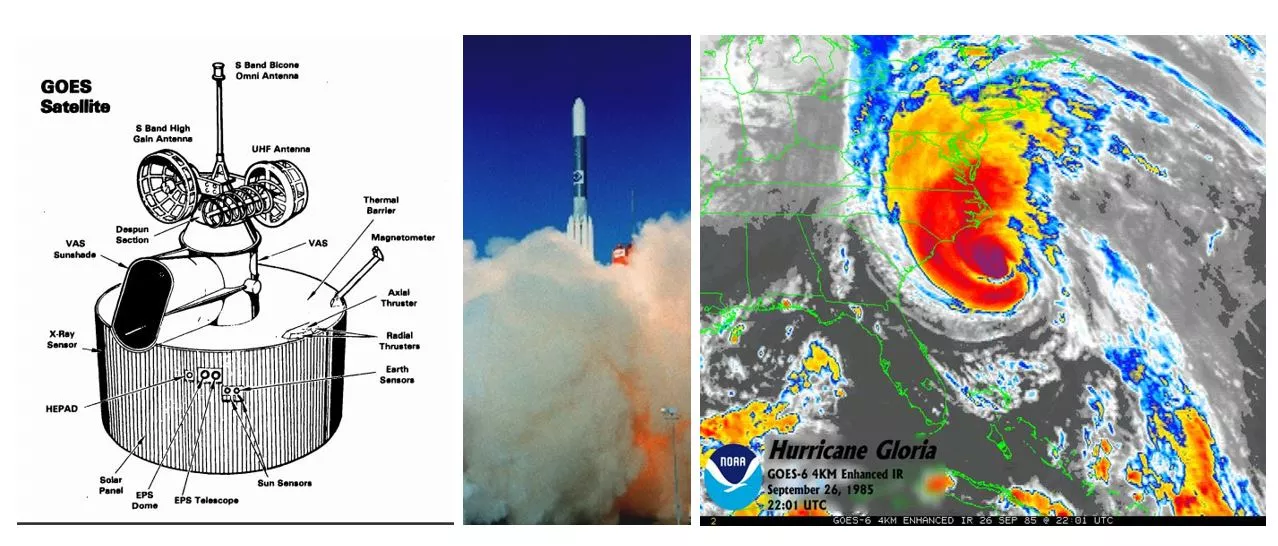
Built with a life expectancy of seven years, GOES-6 remained fully operational for slightly less than six, and remained in orbit for nine. It was deactivated on May 19, 1992.
NOAA's geostationary orbiting environmental satellites (GOES) orbit above the equator at a speed equal to the Earth's rotation, which allows them to hover over one position. In doing so, they continuously provide scientists with detailed weather measurements and frequent imagery used to develop short-term forecasts that help protect life and livelihoods.
For more information, about GOES-6, see the NASA GOES Project Science web page and the document " Satellite Activities of NOAA (1983)." To learn more about the ongoing GOES mission, visit the Office of Satellite and Product Operations.