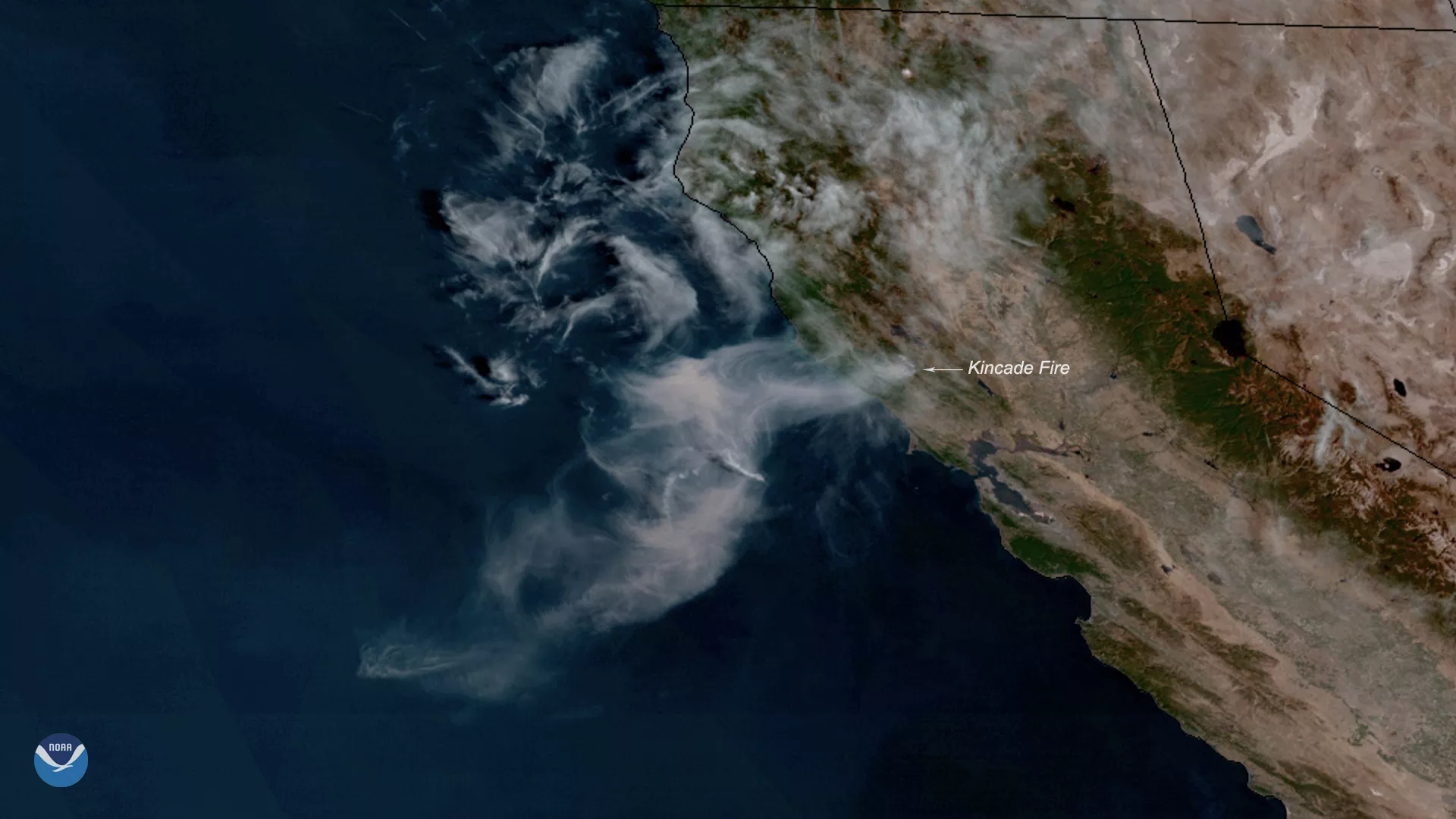
Dust in the Wind
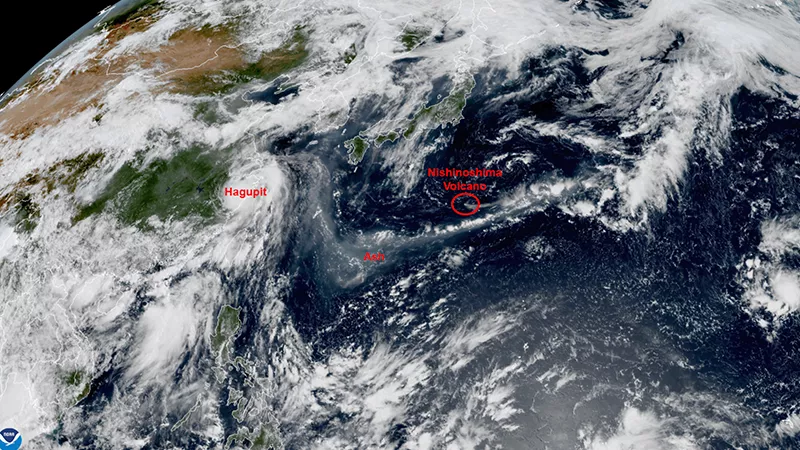
Satellites are important tools for tracking and studying aerosol particles in the atmosphere made of dust, smoke from wildfires, and volcanic ash. These types of particles can not only affect human health and safety but can also affect the weather and climate by cooling or warming the Earth as well as enhancing or preventing cloud formation. Collectively, these phenomena are monitored by special sensors onboard our geostationary satellites.

How we track each one
More Articles on Fire, Dust, and Ash
-
Lightning is a dangerous weather hazard that poses a significant threat to life and property. It…
-
Since mid-May, NOAA satellites have been closely monitoring heat signatures and thick plumes of…
-
On Friday, May 16, 2025, NOAA’s GOES East satellite captured a rare dust storm pushing across…